|
History |
|
Wars & Campaigns |
|
►Boer
War
►First
World War
►►Western
Front
►►►Trench
Warfare: 1914-1916
►►►Allied
Offensive: 1916
►►►Allied
Offensives: 1917
►►►German
Offensive: 1918
►►►Advance
to Victory: 1918
►►Siberia
►Second
World War
►►War
Against Japan
►►North
Africa
►►Italian
Campaign
►►►Sicily
►►►Southern
Italy
►►►The
Sangro and Moro
►►►Battles
of the FSSF
►►►Cassino
►►►Liri
Valley
►►►Advance
to Florence
►►►Gothic
Line
►►►Winter
Lines
►►North-West
Europe
►►►Normandy
►►►Southern
France
►►►Channel
Ports
►►►Scheldt
►►►Nijmegen
Salient
►►►Rhineland
►►►Final
Phase
►Korean
War
►Cold
War
►Gulf
War |
|
Operations |
|
|
|
Battle Honours |
|
Boer War
First World War
Western Front
Trench Warfare: 1914-1916
Allied Offensive: 1916
|
►Somme, 1916 |
1
Jul-18 Nov 16 |
|
►Albert |
.1-13
Jul 16 |
|
►Bazentin |
.14-17
Jul 16 |
|
►Pozieres |
.23
Jul-3 Sep 16 |
|
►Guillemont |
.3-6
Sep 16 |
|
►Ginchy |
.9
Sep 16 |
|
►Flers-Courcelette |
15-22
Sep 16 |
|
►Thiepval |
26-29
Sep 16 |
|
►Le Transloy |
.
1-18 Oct 16 |
Allied
Offensives: 1917
|
►Arras 1917 |
8
Apr-4 May 17 |
|
►Vimy, 1917 |
.9-14
Apr 17 |
|
►Arleux |
28-29 Apr 17 |
|
►Scarpe, 1917 |
.3-4
May17 |
|
►Hill 70 |
.15-25
Aug 17 |
|
►Messines, 1917 |
.7-14
Jun 17 |
|
►Ypres, 1917 |
..31
Jul-10 Nov 17 |
|
►Pilckem |
31
Jul-2 Aug 17 |
|
►Langemarck, 1917 |
.16-18
Aug 17 |
|
►Menin Road |
.20-25
Sep 17 |
|
►Polygon Wood |
26
Sep-3 Oct 17 |
|
►Broodseinde |
.4
Oct 17 |
|
►Poelcapelle |
.9
Oct 17 |
|
►Passchendaele |
.12
Oct 17 |
|
►Cambrai, 1917 |
20
Nov-3 Dec 17 |
German Offensive: 1918
|
►Somme, 1918 |
.21
Mar-5 Apr 18 |
|
►St. Quentin |
.21-23
Mar 18 |
|
►Bapaume, 1918 |
.24-25
Mar 18 |
|
►Rosieres |
.26-27
Mar 18 |
|
►Avre |
.4
Apr 18 |
|
►Lys |
.9-29
Apr 18 |
|
►Estaires |
.9-11
Apr 18 |
|
►Messines, 1918 |
.10-11
Apr 18 |
|
►Bailleul |
.13-15
Apr 18 |
|
►Kemmel |
.17-19
Apr 18 |
Advance to Victory: 1918
|
►Arras, 1918 |
.26
Aug-3 Sep 18 |
|
►Scarpe, 1918 |
26-30 Aug 18. |
|
►Drocourt-Queant |
.2-3
Sep 18 |
|
►Hindenburg Line |
.12
Sep-9 Oct 18 |
|
►Canal du Nord |
.27
Sep-2 Oct 18 |
|
►St. Quentin Canal |
.29
Sep-2 Oct 18 |
|
►Epehy |
3-5
Oct 18 |
|
►Cambrai, 1918 |
.8-9
Oct 18 |
|
►Valenciennes |
.1-2
Nov 18 |
|
►Sambre |
.4
Nov 18 |
|
►Pursuit to Mons |
.28 Sep-11Nov |
Second World War
War Against Japan
South-East Asia
Italian Campaign
Battle of Sicily
Southern
Italy
The Sangro and Moro
Battles of the FSSF
|
►Anzio |
22
Jan-22 May 44 |
|
►Rome |
.22
May-4 Jun 44 |
|
►Advance
|
.22
May-22 Jun 44 |
|
to the Tiber |
. |
|
►Monte Arrestino |
25
May 44 |
|
►Rocca Massima |
27
May 44 |
|
►Colle Ferro |
2
Jun 44 |
Cassino
|
►Cassino II |
11-18
May 44 |
|
►Gustav Line |
11-18
May 44 |
|
►Sant' Angelo in
|
13
May 44 |
|
Teodice |
. |
|
►Pignataro |
14-15 May 44 |
Liri Valley
|
►Hitler Line |
18-24 May 44 |
|
►Melfa Crossing |
24-25 May 44 |
|
►Torrice Crossroads |
30
May 44 |
Advance to Florence
Gothic Line
|
►Gothic Line |
25 Aug-22 Sep 44 |
|
►Monteciccardo |
27-28 Aug 44 |
|
►Point 204 (Pozzo Alto) |
31 Aug 44 |
|
►Borgo Santa Maria |
1 Sep 44 |
|
►Tomba di Pesaro |
1-2 Sep 44 |
Winter Lines
|
►Rimini Line |
14-21 Sep 44 |
|
►San Martino- |
14-18 Sep 44 |
|
San Lorenzo |
. |
|
►San Fortunato |
18-20 Sep 44 |
|
►Sant' Angelo |
11-15 Sep 44 |
|
in Salute |
. |
|
►Bulgaria Village |
13-14 Sep 44 |
|
►Pisciatello |
16-19 Sep 44 |
|
►Savio Bridgehead |
20-23
Sep 44 |
|
►Monte La Pieve |
13-19
Oct 44 |
|
►Monte Spaduro |
19-24 Oct 44 |
|
►Monte San Bartolo |
11-14
Nov 44 |
|
►Lamone Crossing |
2-13
Dec 44 |
|
►Capture of Ravenna |
3-4
Dec 44 |
|
►Naviglio Canal |
12-15 Dec 44 |
|
►Fosso Vecchio |
16-18 Dec 44 |
|
►Fosso Munio |
19-21 Dec 44 |
|
►Conventello- |
2-6 Jan 45 |
|
Comacchio |
. |
Northwest Europe
Battle of Normandy
|
►Quesnay Road |
10-11 Aug 44 |
|
►St. Lambert-sur- |
19-22 Aug 44 |
Southern France
Channel Ports
The Scheldt
Nijmegen Salient
Rhineland
|
►The
Reichswald |
8-13 Feb 45 |
|
►Waal
Flats |
8-15 Feb 45 |
|
►Moyland
Wood |
14-21 Feb 45 |
|
►Goch-Calcar
Road |
19-21 Feb 45 |
|
►The
Hochwald |
26
Feb- |
| . |
4
Mar 45 |
|
►Veen |
6-10 Mar 45 |
|
►Xanten |
8-9
Mar 45 |
Final Phase
|
►The
Rhine |
23
Mar-1 Apr 45 |
|
►Emmerich-Hoch
|
28
Mar-1 Apr 45 |
|
Elten |
. |
Korean War
|
|
Domestic Missions |
|
►FLQ
Crisis |
|
International
Missions |
|
►ICCS
Vietnam 1973
►MFO
Sinai 1986- |
|
Peacekeeping |
|
►UNTEA |
W. N. Guinea 1963-1964 |
|
►ONUCA |
C. America
1989-1992 |
|
►UNTAC |
Cambodia
1992-1993 |
|
►UNMOP |
Prevlaka
1996-2001 |
|
|
Exercises |
|
International
Force in East Timor
The International
Force in East Timor (INTERFET) was a United Nations
peacekeeping mission involving Canadians. The mission ran
concurrently with the United Nations Mission in East Timor
(UNAMET) and was created to provide assistance to that
mission.
Background
East Timor was
colonized by Portugal in the 16th Century and in 1960 the
United Nations placed the colony on its list of
Non-Self-Governing Territories. After promises by Portugal
in 1974 to establish a provisional government, civil war
erupted between pro-independence and anti-independence
factions. Portugal, unable to control the situation,
withdrew. Indonesia responded with a military
intervention, claiming East Timor as a 27th province, but
this annexation was never recognized by the UN.
In 1982, the
United Nations Secretary General began talks with
Indonesia and Portugal to resolve the situation. In Jun
1998, Indonesia proposed autonomy for East Timor within
Indonesia, and a set of agreements were signed in New York
in May 1999. The United Nations, entrusted with the
organization of a consultation with the East Timor people
about autonomy within the Republic of Indonesia,
established the United Nations Mission in East Timor (UNAMET)
on 11 Jun 1999 to carry it out. The mission registered
451,000 voters, and on 30 Aug 1999 some ninety eight
percent of those registered voted to reject the autonomy
in favour of a move towards independence.
The vote resulted
in widespread violence in the region, between
pro-integration militias (sometimes with the help of
security forces from Indonesia) resulting in many deaths
and displacements. In all some 250,000 East Timorese left
or were forced out of the country. Indonesia formally
recognized the result of the vote on 19 Oct 1999.
A Security Council
Mission visit to the region concluded on 12 Sep 1999 and
Indonesia accepted an offer of assistance. INTERFET was
authorized under Australian command, tasked to lend
protection and assistance to UNAMET, as well as the
restoration of peace and security as well as humanitarian
aid.
INTERFET engaged
in humanitarian airdrops, deploying relief workers, and
repatriating citizens from West Timor and other areas in
the absence of Indonesian police, military and
administrative personnel who left after the first
outbreaks of violence.
The United Nations
Transitional Administration in East Timor (UNTAET) was
established in 1999 following the result of the vote and
on 28 Feb 2000, INTERFET handed command of military
operations to that mission.
Mandate
In response to the
deteriorating security and humanitarian situation in East
Timor, INTERFET was created in Sep 1999 in response to
Security Council Resolution 1264 (1999) to re-establish
order in the region. INTERFET began to hand over its
responsibilities to a United Nations mission, the UN
Transitional Administration in East Timor (UNTAET), on 1
Feb 2000 and completed the transition at the end of that
month.
Canadian Military
Involvement
|
Operation
TOUCAN was the Canadian contribution to the
International Force in East Timor (INTERFET) and the
United Nations Transitional Administration in East
Timor (UNTAET). It began in Oct 1999 with the
deployment for six months of 600 Canadian Forces
personnel, including construction engineers from
Esquimalt, BC and Moncton, NB, the 250 sailors of
the replenishment ship HMCS Protecteur, with a
CH-124 Sea King helicopter detachment that completed
157 sorties, a 250-strong Company Group drawn mostly
from the 3e Bataillon, Royal 22e Régiment, and a
tactical airlift detachment of 100 Air Force
personnel and two CC-130 Hercules aircraft from 8
Wing Trenton. During the initial phase of the
operation, when a safe and secure environment was
established and the infrastructure for UNTAET was
put into place, the Canadian contingent provided
security, construction engineering services, airlift
and sealift. During the follow-on phase, Canada
contributed staff officers who worked at UNTAET
Headquarters in Dili, East Timor. |

Soldiers of the Royal 22e Régiment move equipment up
from the beach landing point in Suai, East Timor.
Photo by Cpl Colin Kelley, DND Photo. |
The number of
personnel committed peaked at 650 in late Oct and early
Nov. The 280-strong reinforced infantry company (largely
drawn from 3e Bataillon Royal 22e Régiment) was
transferred to the United Nations Transitional
Administration in East Timor (UNTAET) on 21 Feb 2000,
bringing Canadian participation in INTERFET to a close.
The CBC website
described the mission thusly:
-
The Royal 22nd's
introduction to East Timor is not at all pleasant. True,
there are fewer mortal dangers than in Korea or Bosnia,
but the irritants are innumerable. The daytime brings
scorching heat. The night brings mud, spiders and
scorpions – and the troops are sleeping on the ground.
Monsoon season is coming. And as reporter Mike Smith
reveals...the communications lines are muddier than the
terrain.
-
-
The Van Doos are
part of an international security force called INTERFET,
serving in a battalion of New Zealanders reporting to
Australians. The Van Doos soldiers speak French among
themselves. The locals speak Portuguese or any of 16
indigenous languages. The interpreters are Malaysian.
Getting your point across can be just as difficult as
surviving a night in a "hoochie" without a hammock.
Military Forces
|
Country |
Contribution |
|
Argentina |
50 troops. |
|
Australia |
B Squadron, the 3rd/4th Cavalry Regiment
Air support included, RAAF FA18, F111, FA18, PC9 and P3s.
2 x B707 of 33 Squadron
9 x C-130 of 36 and 37 Squadrons
15 x S-70A of 1st and 5th Aviation Regiments
Bell 206B-1s of 161(R) Squadron
UH-1Hs of 171(GS) Squadron
161 Recce Sqn
No 2 Airfield Defence Squadron (2AFDS) RAAF
2RAR
3rd Australian Brigade
3RAR
5th/7th RAR
Force Prep Unit
SAS
HMAS Adelaide
HMAS Anzac (Frigate)
HMAS Balikpapan (Heavy Landing Craft)
HMAS Brunei (landing craft)
HMAS Darwin
HMAS Farncomb (submarine, landed frogmen at Suai)
HMAS Jervis Bay (Catamaran)
HMAS Labuan
HMAS Success
HMAS Sydney
HMAS Tarakan
HMAS Tobruk (Heavy Lift)
HMAS Waller (submarine, escorted fleet through Timor Sea to Dili)
HMAS Westralia
|
|
Brazil |
30 to 50 military police. |
|
Canada |
600 military personnel on
a a six-month tour.
250 sailors from HMCS
Protecteur Naval replenishment ship
250-strong light infantry
company group largely from the 3rd Battalion, Royal 22e Régiment
Approximately 100 air force
personnel with two CC-130 Hercules transport aircraft from 8 Wing Trenton. |
|
Denmark |
? |
|
Egypt |
? |
|
Fiji |
191 troops attached to New Zealand units |
|
France |
500 troops and a frigate to the region, also one field surgery, including 12 surgeons and two doctors.
3 x C-130
4 x Puma
FNS Vendemiaire (frigate), later relieved by FNS
Prairial (frigate)
FNS Siroco (Dock landing Ship)
French Marines. |
|
Germany |
Medical unit (100 troops) |
|
Ireland |
ARW detachment numbering
30 personnel, known as the No. 1 Irish Contingent.
The Irish Component Headquarters
will be supported by the National Support Element, (NSE). |
|
Italy |
600 military personnel,
including tactical group of 200 paratroops, transport aircraft and amphibious
naval unit on a vessel with hospital facilities, on-board helicopters and
transport aircraft |
|
Jordan |
Over 700 Jordanian troops
arrived during Interfet and replaced Australian troops in the Oecussi enclave
of East Timor in February 2000. |
|
Kenya |
1 Army Company
Medical unit (100 troops)
|
|
Malaysia |
Malaysia has said it will
send a team of military officers to join the multinational force, after
earlier refusing because of Australia's leading role. |
|
Mozambique |
? |
|
Nepal |
158 troops attached to NZ units at Suai, At least three troops killed. |
|
New Zealand |
5 Iroqois helicopters of No.3 squadron at Suai, East Timor.
Hercules and Boeing transport
aircraft of No.40 Squadron provide regular re-supply flights to and from
East Timor.
2 x C-130
RNZAF chartered a 747 in Sept ‘99.
3200 NZ military
personnel served in ET divided into 6 Battalion Groups, with only one
serving at a time, and rotating at 6 month intervals. (The force being
made up from both the Regular and Territorial Forces of all service
arms)
The NZSAS were also used in Timor.
NZ Supplied 19 Customs Officers for border control service in Timor.
NZ supplied over 45 Police and Prison Officers for service in Timor.
There were at least 12 Ministry of Agriculture & Fisheries (MAF) staff seconded for quarantine duties in Timor.
A private Airline
(Vincent Airline) supplied one aircraft and 6 crew for the transporting
of military personnel between Timor and Darwin, Australia.
NZ supplied the following military ships -
HMNZS Canterbury (Approx 250 crew).
HMNZS Te Kaha (Approx 170 crew).
HMNZS Endeavour (Approx 35 crew).
MV Edisongracht chartered by NZ to carry freight and equipment.
MV Edamgracht chartered by NZ to carry freight and equipment.
4 NZ peacekeepers lost their lives as a result of their service in Timor.
|
|
Norway |
Five officers. |
|
Philippines |
1,200 army engineers, medical and other support troops to the multinational peacekeeping force.
2 x C-130
Elements of Scout Ranger Regiment
|
|
Republic of Korea |
400-stong infantry battalion
to East Timor in what would be the first ever deployment of South Korean
combat troops for peacekeeping operations abroad. |
|
Singapore |
Medical detachment
1 x C-130
RSS Excellence (LST)
RSS Perseverance (LST)
RSS Intrepid (LST)
|
|
Sweden |
Civilian police officers
and $1.2m in aid. |
|
Thailand |
Ultimately to deploy more
than 1,000 personnel, including combat troops, engineers, medics and technicians.
Thai Major-General Songkitti Chakkrabhat is the mission's deputy commander. |
|
United Kingdom |
2 x C-130
1 x VC-10
HMS Glasgow
270 Gurkhas from 2 Royal Gurkha Rifles
Party of SBS troops. |
|
United States |
200 military personnel,
half of whom will serve on the ground in East Timor, and support from Pacific
Fleet. The US also transported troops from other nations and helped with
logistics, communications and intelligence.
1 x EP-3C based at RAAF Tindal
Members of the US Marines
US Marine Sea Stallion Helicopters
USS Belleau Wood
(LHA 3)
USNS Kilauea (T-AE
26) ammunition ship. USS Mobile Bay (Cruiser)
USS Pelelieu
USS San Jose
|
Insignia
|
|
The
Government of Australia established the INTERFET
Medal for military personnel who participated in the
mission lasting from Oct 1999 to Apr 2000.
|
The qualifying
period of service is 30 days cumulative service in the
area of operations, and the area of operations for CF
personnel included East Timor, the sea adjacent to East
Timor to a distance of 12 nautical miles; and the CF
staging base at Darwin, Australia.
Approximately 760
have been awarded to members of the Canadian Forces. The
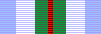
ribbon colours are drawn from white, green and blue
representing the [Australian] Navy, Army and Air Force,
but having dual representations of:
-
white for peace
-
blue for the sea
surrounding East Timor
-
green for the
regrowth of a new nation
-
The red stripe
represented the turbulent past of East Timor
|
